通常是因为更新系统后,ca证书没有被更新,新的证书被命名为“.rpmnew”,解决办法是删掉旧证书,重新安装新的证书。
rm -f /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt && yum reinstall -y ca-certificates通常是因为更新系统后,ca证书没有被更新,新的证书被命名为“.rpmnew”,解决办法是删掉旧证书,重新安装新的证书。
rm -f /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt && yum reinstall -y ca-certificateshosts文件是不允许包含其他文件的,但是可以通过其他方案实现:
保存一个hosts.base一个hosts.local,然后通过脚本合并成为hosts文件
通过bind搭建私有服务器
通过pssh, ansible 等运维工具同步配置,可以和方法一一起用
统计代码行数
find . \
\( -path ./web -o -path ./runtime -o -path ./config \) -prune -o \
\( -name "*.php" -o -name "*.js" -o -name "*.css" -o -name "*.scss" \) \
| xargs wc -lweb,runtime,config为需要排除的目录
php,js,css,scss为源码文件扩展名
查找所有文件类型为php且文件名包含config大小写,
且文件内容oldstring替换为newstring
find -name '*.php' | grep -i config | xargs sed -i 's/oldstring/newstring/g'可用于linux/mac,可以增量,不能跨机器。
使用-u参数实现增量,-r递归,使用实例
cp -ru dir1/* dir2/详细参数
用法:cp [选项]... [-T] 源文件 目标文件
或:cp [选项]... 源文件... 目录
或:cp [选项]... -t 目录 源文件...
将源文件复制至目标文件,或将多个源文件复制至目标目录。
长选项必须使用的参数对于短选项时也是必需使用的。
-a, --archive 等于-dR --preserve=all
--backup[=CONTROL 为每个已存在的目标文件创建备份
-b 类似--backup 但不接受参数
--copy-contents 在递归处理是复制特殊文件内容
-d 等于--no-dereference --preserve=links
-f, --force 如果目标文件无法打开则将其移除并重试(当 -n 选项
存在时则不需再选此项)
-i, --interactive 覆盖前询问(使前面的 -n 选项失效)
-H 跟随源文件中的命令行符号链接
-l, --link 链接文件而不复制
-L, --dereference 总是跟随符号链接
-n, --no-clobber 不要覆盖已存在的文件(使前面的 -i 选项失效)
-P, --no-dereference 不跟随源文件中的符号链接
-p 等于--preserve=模式,所有权,时间戳
--preserve[=属性列表 保持指定的属性(默认:模式,所有权,时间戳),如果
可能保持附加属性:环境、链接、xattr 等
-c same as --preserve=context
--sno-preserve=属性列表 不保留指定的文件属性
--parents 复制前在目标目录创建来源文件路径中的所有目录
-R, -r, --recursive 递归复制目录及其子目录内的所有内容
--reflink[=WHEN] 控制克隆/CoW 副本。请查看下面的内如。
--remove-destination 尝试打开目标文件前先删除已存在的目的地
文件 (相对于 --force 选项)
--sparse=WHEN 控制创建稀疏文件的方式
--strip-trailing-slashes 删除参数中所有源文件/目录末端的斜杠
-s, --symbolic-link 只创建符号链接而不复制文件
-S, --suffix=后缀 自行指定备份文件的后缀
-t, --target-directory=目录 将所有参数指定的源文件/目录
复制至目标目录
-T, --no-target-directory 将目标目录视作普通文件
-u, --update copy only when the SOURCE file is newer
than the destination file or when the
destination file is missing
-v, --verbose explain what is being done
-x, --one-file-system stay on this file system
-Z, --context=CONTEXT set security context of copy to CONTEXT
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
--version 显示版本信息并退出可用于linux/mac系统,可以增量,可以跨机器,跨机器通过ssh。
使用实例
scp user@host1:/dir/* /home/www/详细参数
usage: scp [-1246BCpqrv] [-c cipher] [-F ssh_config] [-i identity_file]
[-l limit] [-o ssh_option] [-P port] [-S program]
[[user@]host1:]file1 ... [[user@]host2:]file2
-B 使用批处理模式(传输过程中不询问传输口令或短语)
-C 允许压缩。(将-C标志传递给ssh,从而打开压缩功能)
-p 保留原文件的修改时间,访问时间和访问权限。
-q 不显示传输进度条。
-r 递归复制整个目录。
-v 详细方式显示输出。scp和ssh(1)会显示出整个过程的调试信息。这些信息用于调试连接,验证和配置问题。
-c cipher 以cipher将数据传输进行加密,这个选项将直接传递给ssh。
-F ssh_config 指定一个替代的ssh配置文件,此参数直接传递给ssh。
-i identity_file 从指定文件中读取传输时使用的密钥文件,此参数直接传递给ssh。
-l limit 限定用户所能使用的带宽,以Kbit/s为单位。
-o ssh_option 如果习惯于使用ssh_config(5)中的参数传递方式,
-P port 注意是大写的P, port是指定数据传输用到的端口号
-S program 指定加密传输时所使用的程序。此程序必须能够理解ssh(1)的选项。可用于linux/mac系统,可以增量,可以跨机器,跨机器通过ssh。相对于scp推荐。可以显示进度、排除软链等。
用例
rsync -e "ssh -p22222" -avpgolr --progress host:/dir/file /dir/file详细参数
Usage: rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... DEST
or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST:DEST
or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST::DEST
or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST
or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST]
or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST::SRC [DEST]
or rsync [OPTION]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC [DEST]
The ':' usages connect via remote shell, while '::' & 'rsync://' usages connect
to an rsync daemon, and require SRC or DEST to start with a module name.
Options
-v, --verbose increase verbosity
-q, --quiet suppress non-error messages
--no-motd suppress daemon-mode MOTD (see manpage caveat)
-c, --checksum skip based on checksum, not mod-time & size
-a, --archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X)
--no-OPTION turn off an implied OPTION (e.g. --no-D)
-r, --recursive recurse into directories
-R, --relative use relative path names
--no-implied-dirs don't send implied dirs with --relative
-b, --backup make backups (see --suffix & --backup-dir)
--backup-dir=DIR make backups into hierarchy based in DIR
--suffix=SUFFIX set backup suffix (default ~ w/o --backup-dir)
-u, --update skip files that are newer on the receiver
--inplace update destination files in-place (SEE MAN PAGE)
--append append data onto shorter files
--append-verify like --append, but with old data in file checksum
-d, --dirs transfer directories without recursing
-l, --links copy symlinks as symlinks
-L, --copy-links transform symlink into referent file/dir
--copy-unsafe-links only "unsafe" symlinks are transformed
--safe-links ignore symlinks that point outside the source tree
-k, --copy-dirlinks transform symlink to a dir into referent dir
-K, --keep-dirlinks treat symlinked dir on receiver as dir
-H, --hard-links preserve hard links
-p, --perms preserve permissions
-E, --executability preserve the file's executability
--chmod=CHMOD affect file and/or directory permissions
-A, --acls preserve ACLs (implies --perms)
-X, --xattrs preserve extended attributes
-o, --owner preserve owner (super-user only)
-g, --group preserve group
--devices preserve device files (super-user only)
--copy-devices copy device contents as regular file
--specials preserve special files
-D same as --devices --specials
-t, --times preserve modification times
-O, --omit-dir-times omit directories from --times
--super receiver attempts super-user activities
--fake-super store/recover privileged attrs using xattrs
-S, --sparse handle sparse files efficiently
-n, --dry-run perform a trial run with no changes made
-W, --whole-file copy files whole (without delta-xfer algorithm)
-x, --one-file-system don't cross filesystem boundaries
-B, --block-size=SIZE force a fixed checksum block-size
-e, --rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use
--rsync-path=PROGRAM specify the rsync to run on the remote machine
--existing skip creating new files on receiver
--ignore-existing skip updating files that already exist on receiver
--remove-source-files sender removes synchronized files (non-dirs)
--del an alias for --delete-during
--delete delete extraneous files from destination dirs
--delete-before receiver deletes before transfer, not during
--delete-during receiver deletes during transfer (default)
--delete-delay find deletions during, delete after
--delete-after receiver deletes after transfer, not during
--delete-excluded also delete excluded files from destination dirs
--ignore-errors delete even if there are I/O errors
--force force deletion of directories even if not empty
--max-delete=NUM don't delete more than NUM files
--max-size=SIZE don't transfer any file larger than SIZE
--min-size=SIZE don't transfer any file smaller than SIZE
--partial keep partially transferred files
--partial-dir=DIR put a partially transferred file into DIR
--delay-updates put all updated files into place at transfer's end
-m, --prune-empty-dirs prune empty directory chains from the file-list
--numeric-ids don't map uid/gid values by user/group name
--timeout=SECONDS set I/O timeout in seconds
--contimeout=SECONDS set daemon connection timeout in seconds
-I, --ignore-times don't skip files that match in size and mod-time
--size-only skip files that match in size
--modify-window=NUM compare mod-times with reduced accuracy
-T, --temp-dir=DIR create temporary files in directory DIR
-y, --fuzzy find similar file for basis if no dest file
--compare-dest=DIR also compare destination files relative to DIR
--copy-dest=DIR ... and include copies of unchanged files
--link-dest=DIR hardlink to files in DIR when unchanged
-z, --compress compress file data during the transfer
--compress-level=NUM explicitly set compression level
--skip-compress=LIST skip compressing files with a suffix in LIST
-C, --cvs-exclude auto-ignore files the same way CVS does
-f, --filter=RULE add a file-filtering RULE
-F same as --filter='dir-merge /.rsync-filter'
repeated: --filter='- .rsync-filter'
--exclude=PATTERN exclude files matching PATTERN
--exclude-from=FILE read exclude patterns from FILE
--include=PATTERN don't exclude files matching PATTERN
--include-from=FILE read include patterns from FILE
--files-from=FILE read list of source-file names from FILE
-0, --from0 all *-from/filter files are delimited by 0s
-s, --protect-args no space-splitting; only wildcard special-chars
--address=ADDRESS bind address for outgoing socket to daemon
--port=PORT specify double-colon alternate port number
--sockopts=OPTIONS specify custom TCP options
--blocking-io use blocking I/O for the remote shell
--stats give some file-transfer stats
-8, --8-bit-output leave high-bit chars unescaped in output
-h, --human-readable output numbers in a human-readable format
--progress show progress during transfer
-P same as --partial --progress
-i, --itemize-changes output a change-summary for all updates
--out-format=FORMAT output updates using the specified FORMAT
--log-file=FILE log what we're doing to the specified FILE
--log-file-format=FMT log updates using the specified FMT
--password-file=FILE read daemon-access password from FILE
--list-only list the files instead of copying them
--bwlimit=KBPS limit I/O bandwidth; KBytes per second
--write-batch=FILE write a batched update to FILE
--only-write-batch=FILE like --write-batch but w/o updating destination
--read-batch=FILE read a batched update from FILE
--protocol=NUM force an older protocol version to be used
--iconv=CONVERT_SPEC request charset conversion of filenames
-4, --ipv4 prefer IPv4
-6, --ipv6 prefer IPv6
--version print version number
(-h) --help show this help (-h works with no other options)DRBD是linux的内核的存储层中的一个分布式存储系统,可用使用DRBD在两台Linux服务器之间共享块设备,共享文件系统和数据。
用于linux/mac,类似于一个网络RAID-1的功能,高性能。
1、先安装好inotify包
wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
tar zxf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
cd inotify-tools-3.14
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify-3.14
make && make install2、创建监控脚本inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
#para
host01=192.168.0.144 #rsync服务器地址
src=/backup #本地监控的目录
dst=backup #rsync服务器的模块名称
user=nowview #rsync服务器的虚拟用户
rsync_passfile=/etc/rsyncd.password #本地调用rsync服务的密码文件
inotify_home=/usr/local/inotify-3.14 #inotify的安装目录
#judge
if [ ! -e "$src" ] \
|| [ ! -e "${rsync_passfile}" ] \
|| [ ! -e "${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait" ] \
|| [ ! -e "/usr/bin/rsync" ];
then
echo "Check File and Folder"
exit 9
fi
${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f' -e close_write,delete,create,attrib $src \
| while read file
do
# rsync -avzP --delete --timeout=100 --password-file=${rsync_passfile} $src $user@$host01::$dst >/dev/null 2>&1
cd $src && rsync -aruz -R --delete ./ --timeout=100 $user@$host01::$dst --password-file=${rsync_passfile} >/dev/null 2>&1
done
exit 0lsyncd 是一个支持实时、双向、多机器的多模式文件同步工具。
使用 Lua 语言封装了 inotify 和 rsync 工具,采用了 Linux 内核(2.6.13 及以后)里的 inotify 触发机制,然后通过 rsync 去差异同步,达到实时的效果。
支持Windows/linux/mac/android,采用go语言开发,提供多个平台的客户端。没有iOS客户端。
同样采用go开发,Seafile 是一款开源的企业云盘,注重可靠性和性能。支持 Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android 平台。支持文件同步或者直接挂载到本地访问。
采用PHP基于ownCloud开发,支持 Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android 平台。
uname -r如果内核版本大于等于4.9可以直接开启
然后使用命令modinfo tcp_bbr查看内核模块是否存在。
modinfo tcp_bbrsudo modprobe tcp_bbr默认没有开启,自动开启
echo "tcp_bbr" > /etc/modules-load.d/80-bbr.conf
echo "net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=bbr" >> /etc/sysctl.d/80-bbr.conf
echo "net.core.default_qdisc=fq" >> /etc/sysctl.d/80-bbr.confsysctl -p sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_controldnf update -y
dnf install supervisor
sytemctl enable supervisord
vim /etc/supervisor/xxx.conf
[program:testprogram]
directory = /root/go/src/test
command = /root/go/src/test/bin/server
autostart = true
startsecs = 5
autorestart = true
startretries = 3
user = root
redirect_stderr = true
stdout_logfile = /var/log/supervisor/test.logsupervisorctl reload
supervisorctl start xxx
supervisorctl statushttps://github.com/tengattack/certbot-dns-aliyun
certbot certonly -a certbot-dns-aliyun:dns-aliyun \
--certbot-dns-aliyun:dns-aliyun-credentials /data/aliyun.ini \
-d c4ys.com \
-d *.c4ys.com
https://github.com/tengattack/certbot-dns-dnspod
certbot certonly -a certbot-dns-dnspod:dns-dnspod \
--certbot-dns-dnspod:dns-dnspod-credentials /data/aliyun.ini \
-d c4ys.com \
-d *.c4ys.comcertbot pluginscertbot renew
自动重新加载nginx(需要更新成功后,所以等前一个任务进行几分钟之后再执行)
nginx -s reload(CentOS、Ubuntu、MacOS 都支持,但只有5位数随机)
echo $RANDOM
24308
(CentOS、Ubuntu支持,MacOS不支持纳秒 +%N)
date +%s%N
1557366636971317933
(CentOS、Ubuntu、MacOS 都支持)
head -20 /dev/urandom | cksum | cut -f1 -d " "
1053195602
(CentOS、Ubuntu支持,MacOS不支持)
cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid
bf05d41c-d69e-4247-8a79-baf3ab3f98ed
(CentOS、Ubuntu支持、MacOS 都支持,需安装 openssl,推荐)
openssl rand -base64 128
Smt+jcaMSQ64Y4La8U6OUFl/TZWm+cKGtDqg+MRbKY6Zwp5iOzg3xoVZv+6NQv/W
UL+sqAHBhbTD1ZPgsyeloxTVLRV/SjU2O/mJAZoFLLZXtDhldl5lfgz3s3s28R+u
24TUNXnxGLGqQQxaudcF8Lhgq3LjDLQWzrgrTOIv1e0=
openssl rand -base64 128 | md5sum | cut -c1-32
2cbb48ea9bac4b08c2a9b4518e1faf79
openssl rand -hex 16
339a905406bb4ef3631dfa1ad67d8d6a
openssl rand -hex 8 | cksum
307618125 17
openssl rand -hex 8 | cksum | cut -c1-8
41657201
使用Files(又名Nautilus)时,您是否想过快速打开终端以在当前位置运行命令?
Nautilus的gnome-terminal-nautilus附加组件提供了一个右键单击上下文菜单项, 可以在当前位置快速打开一个新的gnome-terminal窗口。
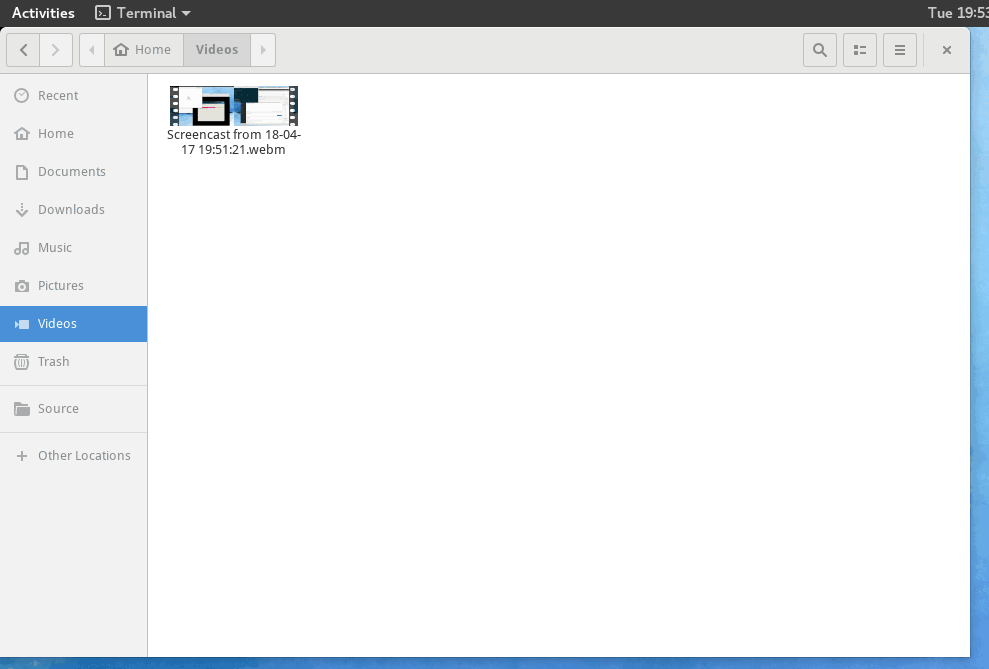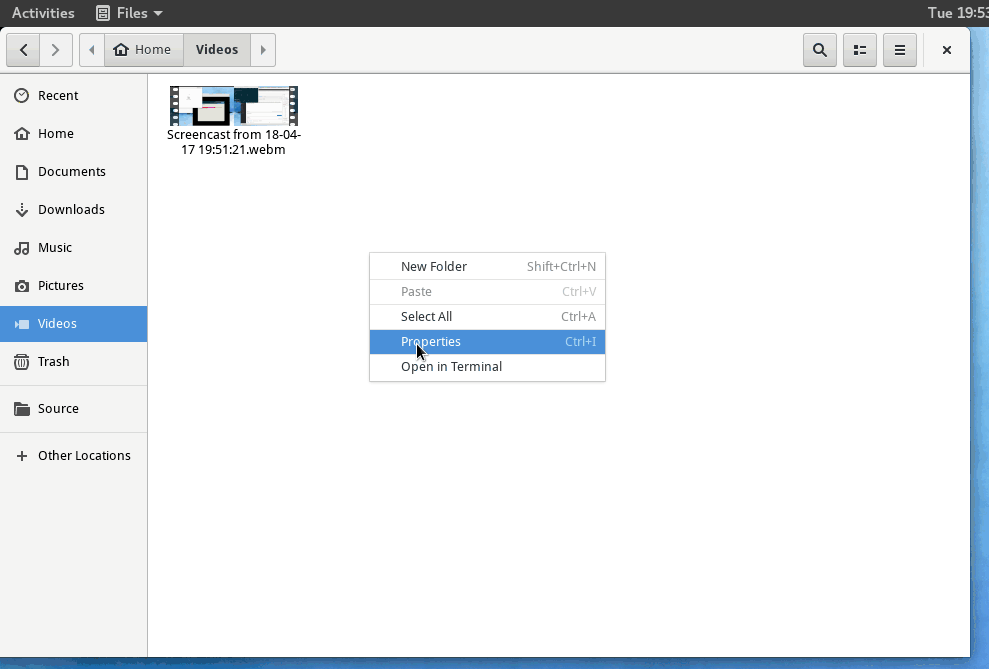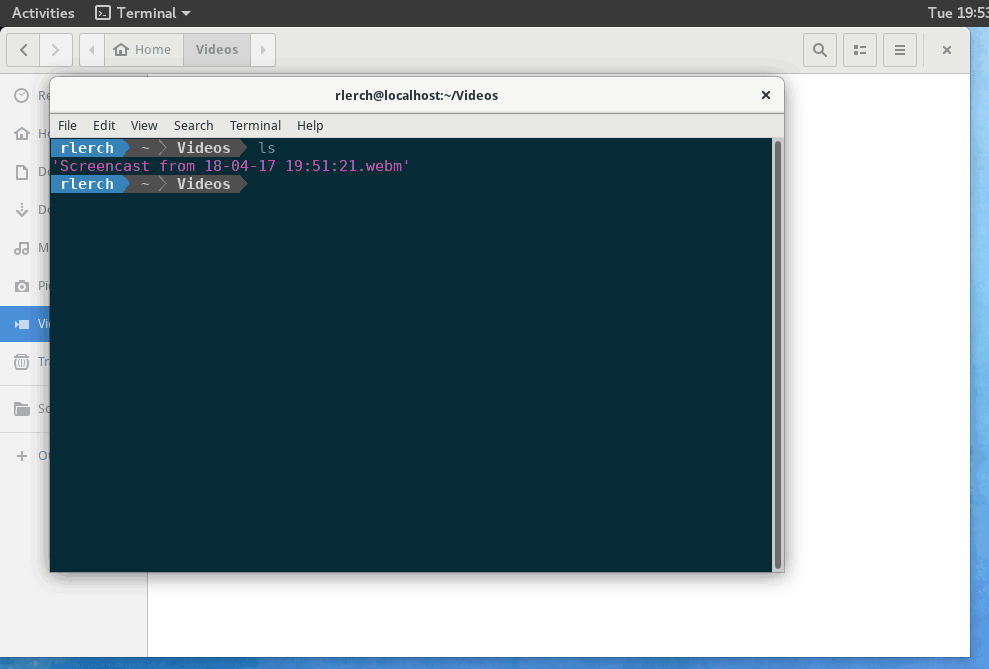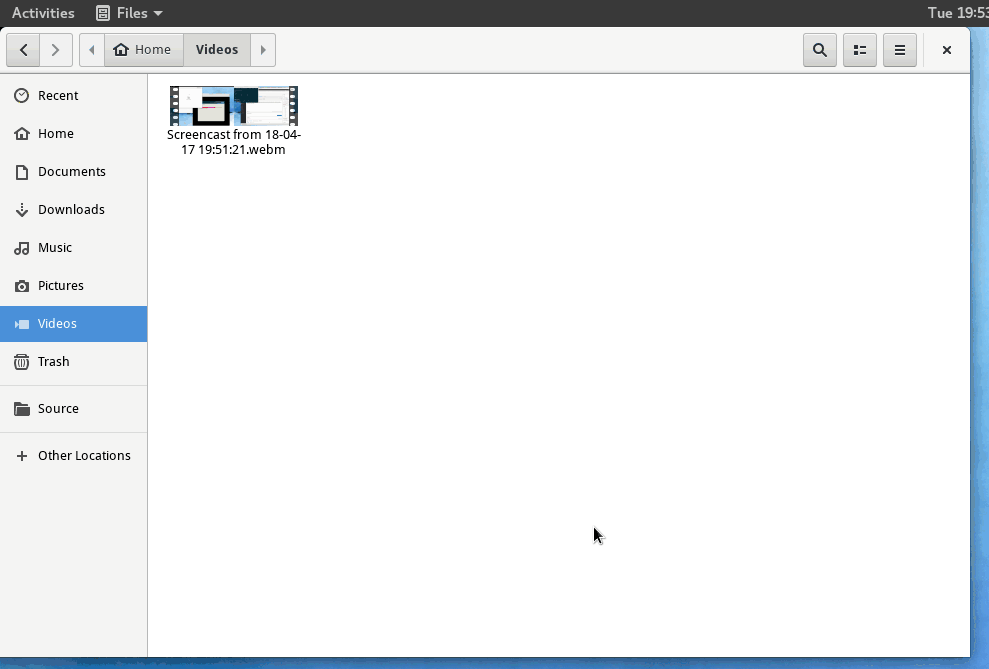
当您需要对图形文件浏览器中正在查看的某些文件运行快速命令时,对nautilus界面的这一小调整非常方便。
sudo dnf install gnome-terminal-nautilus
安装后,“在终端中打开”选项应出现在“文件”中的右键单击上下文菜单中。如果安装后没有出现,请通过运行以下命令强制关闭Nautilus。然后重新打开文件
nautilus -q